This article is part of a four-part series on What is BACnet, you can access the other parts below:
BACnet Part 1: BACnet Overview
BACnet Part 2: Communication 101
BACnet Part 4: BACnet/MSTP
BACnet is the most prevelant protocol in the building automation space but to many it is a six letter word that screams confusion!
In this series we will dig deep into what BACnet really is and what it isn't at the end of this mini-course you will be able to confidently communicate:
- What BACnet is
- Why It is used
- How it applies to you
Part 3: BACnet/IP
In What is BACnet Part 2 I covered an overview of the BACnet communication framework. In this article I will go in depth on BACnet/IP communication.
BACnet/IP
BACnet over IP is a method from which BACnet/ Ethernet packets can use the framework of the UDP/IP protocol to send data to BACnet devices across multiple subnets. For those who are less IT savvy BACnet/IP allows messages that typically could only communicate on one network to communicate across multiple networks. This article will discuss several key topics.
- What is a TCP/IP and UDP/IP
- Why do we use BACnet/IP
- How does BACnet/IP communicate?
- Where is BACnet/IP Practical?
- How is BACnet/IP different then BACnet/Ethernet
Key Terms
- UDP-User Datagram Protocol
- TCP- Transmission Control Protocol
- IP- Internet Protocol
- Subnet- A logical subdivision of an IP network.
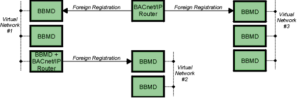
- BBMD- (BACnet Broadcast Management Device)- Allows the broadcast message "Who is/I am" to be transmitted across subnets.
- MAC Address- (Media Access Control)- This is a hardware identification for the device. In IP this MAC address is assigned a specific IP address.
- Static Address- This is an IP address that is set for a specific MAC address
- Dynamic Address- This is an IP address that is leased to a specific or series MAC address.
- Routing- This is the process of transmitting an IP message between different subnets.
What is TCP/IP and UDP/IP
TCP/IP and UDP/IP are protocols that allows messages to communicate across multiple Subnets.
IP:
- Allows for transmission of data
- Applies addresses to devices
- Allows for the creation of logical subnets
UDP:
- Connection-less protocol
- Allows for small packets that are non network intensive.
TCP:
- Verifies data transmission
- Has built in error correction
Why do we use BACnet/IP?
BACnet over Ethernet allowed building automation systems to transfer data via ethernet across a Bus architecture this worked well initially but with the advent of the internet and the desire to have a single control system across a network of buildings the need for networks larger then 254 nodes was needed. That is why ASHRAE adopted BACnet/IP in annex j of the 135- 1995 standard.
BACnet IP allows us to:
- Communicate across multiple subnets
- Create multi-campus control systems
- Utilize the benefits of fiber and giga-ethernet.
- Assign IP addresses to our BACnet devices making the web accessible.
How does BACnet/IP communicate?
BACnet/IP communicates using four methods.
- BACnet/IP to BACnet/IP (same subnet): In this situation the location of the two devices is already known by the host and the message is routed to the device using a local switch.
- BACnet/IP to BACnet/IP (different subnet): In this situation the location of the two devices is already known by the host and the message is routed to the device using switches and routers.
- Broadcast (same subnet): This is a standard Who is/ I am message sent across a local subnet for the BBMD to discover what the address are for the BACnet devices on the subnet.
- Broadcast (different subnet): This is a standard Who is/ I am message sent across a local subnet for the BBMD to discover what the address are for the BACnet devices on other subnets.
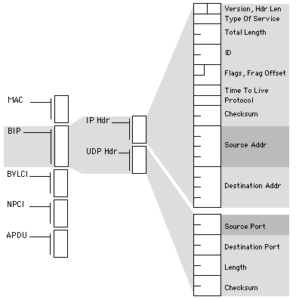
BACnet/IP uses a packet structure similar to a TCP/UDP Packet to pass messages from one device to another. A detailed description of a BACnet/IP packet is below.
Where is BACnet/IP Practical?
Not many vendors still use solely BACnet/Ethernet as most have adopted the BACnet/IP framework. Thus the ultimate answer is that BACnet/IP is practical for any solely BACnet system. The true choice on BACnet/IP is when you are utilizing a non native platform such as Tridium from which you have multiple protocol choices.
Conclusion
This article covered the subject of BACnet/IP Communications. In this article you learned:
- Key features of BACnet/IP messaging
- What TCP and UDP are
- Why BACnet/IP is used and how it works
- How a BBMD works
So what else do you need to learn about BACnet?
Do you have a specific question?
Ask me below in the comments!